Let’s do some math!
Measure Fractions on Number Lines
EMC Video — Review and Preview Fractions on Number Lines
Measurement bars on number lines are a particularly useful representation to review fraction concepts from grades 3-5 and apply those concepts to grades 6-8 rational number concepts. For example, once students understand how to identify and apply unit fraction bars to represent positive fractions to the right of zero, the same strategy can be used to measure negative fractions to the left of zero. In addition, measurement bars on number lines are useful to review:
Equivalent fractions
Common denominators
Addition and subtraction of fractions
Multiplying fractions
Students can apply these measurement bar strategies to:
Represent positive and negative fractions and decimals
Represent and solve rate problems on double number lines
Represent and solve percent problems on percent bars
Divide fractions
Apply operations to positive and negative fractions
Measure to Locate and Label Fractions on Number Lines
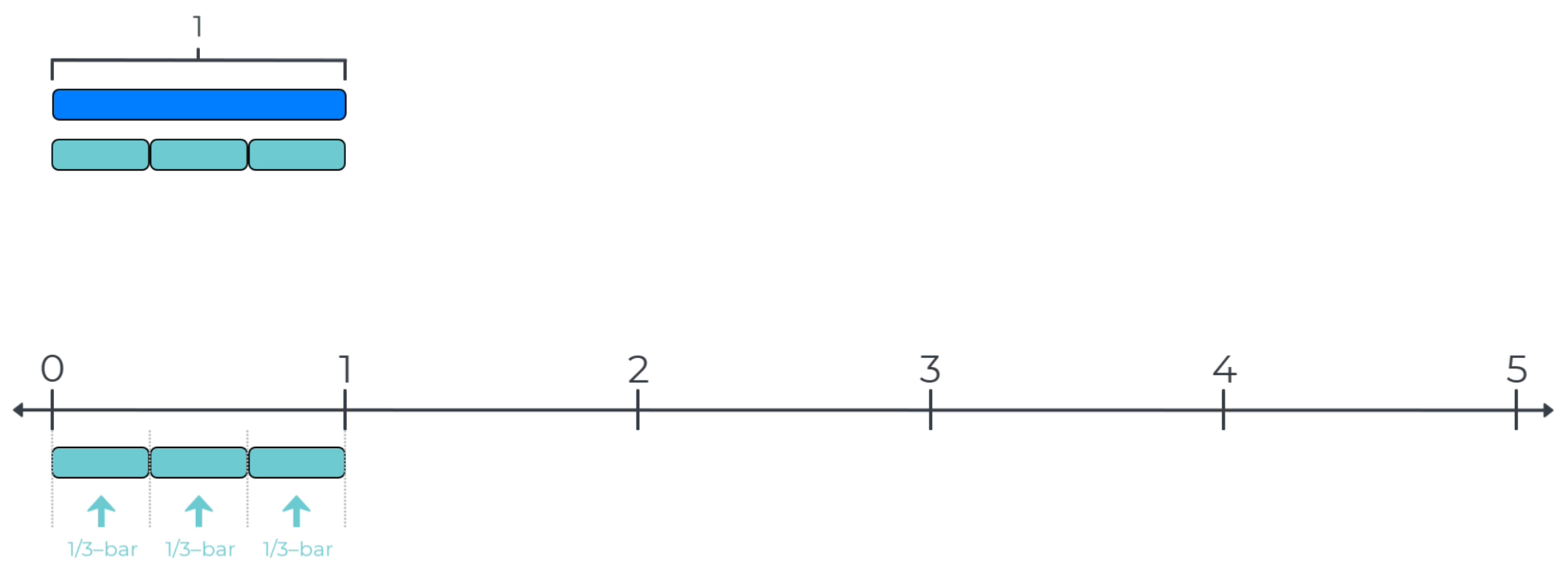
Problem-Solving Talks review the use of unit-fraction-bars to measure and label points that fall between whole numbers on number lines. Unit-fraction-bars are sets of equal-length bars that measure a length of 1. In the example below, three equal-length bars measure the same length as a 1-bar in the measurement key. So, each equal-length bar is a unit-fraction-bar that measures a length of 1/3, which can be called a 1/3-bar. Remind students that unit fractions always have a 1 in the numerator of the fraction.
On the number line, one 1/3-bar measures from zero to 1/3, and two 1/3-bars measure from zero to 2/3.
By definition, three 1/3-bars or 3/3 measures from zero to the tick mark for 1. Numbers that measure to the same point on a number line are defined to be equivalent.
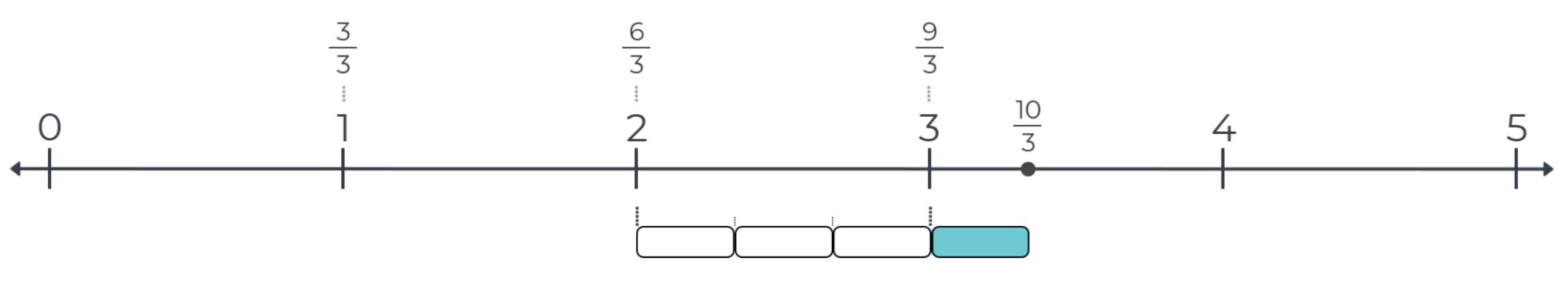
Unit fraction bars are also used to measure fractions greater than 1.
Because the Magnetic Whiteboard Manipulative Kit only contains enough unit fraction bars to measure from zero to 2 on this number line, fraction strips in the manipulative kit are used to measure fractions greater than 2. In the example below, the fraction strip is used to skip count to measure 3/3, 6/3, and 9/3. Then, one additional 1/3-bar measures to 10/3.
Represent Equivalent Fractions with Unit Fraction Bars
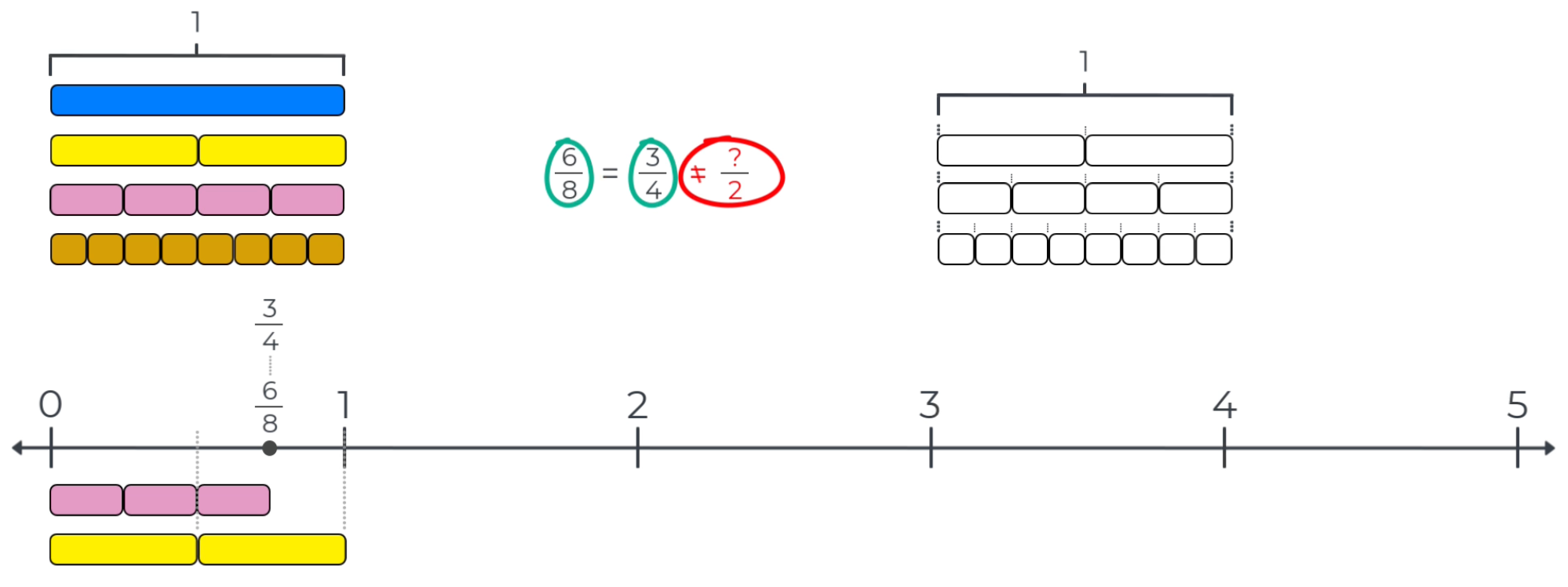
Measurement strategies on number lines can be used to identify equivalent fractions. Two equivalent numbers measure from zero to the same point on the number line. In the example below, three 1/4-bars and six 1/8-bars measure from zero to the same point on the number line, which demonstrates that 3/4 is equivalent to 6/8.
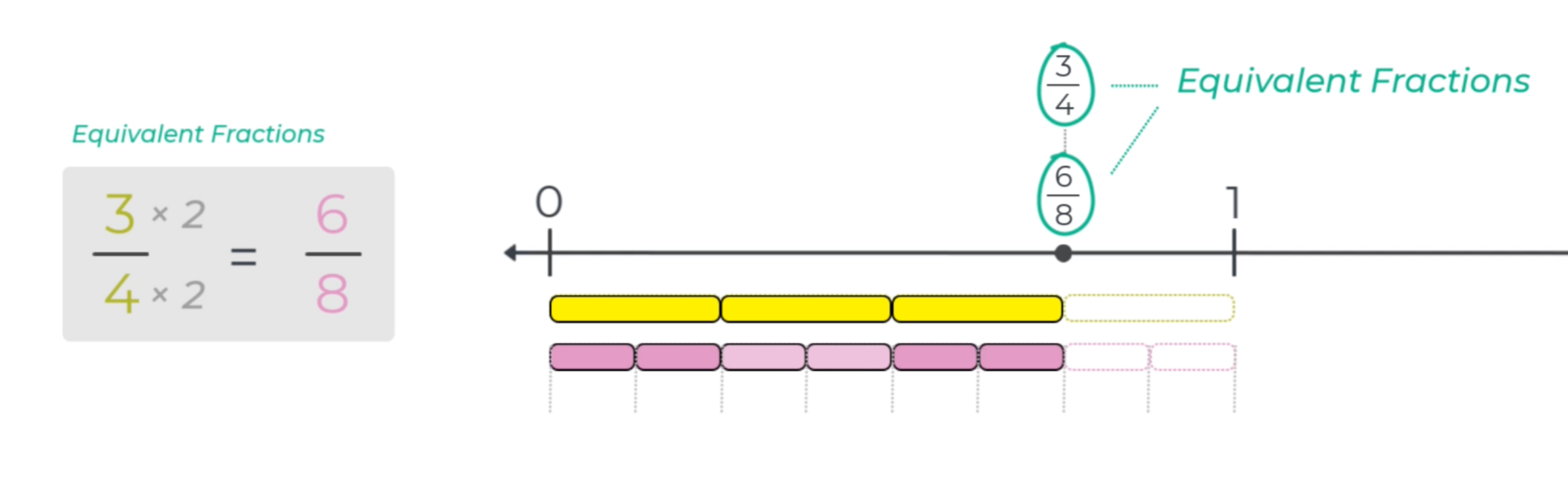
This intuitive definition of equivalent fractions—fractions that measure from zero to the same point on a number line—will be a powerful tool when students learn procedures for fractions in subsequent grade levels. In the example below, each of the three 1/4-bar is split into two equal parts so that six 1/8-bars measure from zero to the same point on the number line. Note that multiplying the numerator and denominator by 5 generates the same result. If the three 1/4-bar is split into 5 equal parts, multiplying the numerator and denominator by 5 would generate the same result.
So, the unit fraction representation of fractions on number lines will also be useful to help students make sense of the procedure to generate equivlent fractions. Similar strategies will be applied to help students make sense of common denominators and addition of fractions.
The 1/2-bars can be used to show that there is no simple fraction with a denominator of 2 that is equivalent to 3/4 and 6/8. This is because one 1/2-bar measures to a point that is closer to zero than the point for 3/4 = 6/8. And, two 1/2-bars measure to a point that is further from zero than the point for 3/4 = 6/8.
Measure to Locate Negative Fractions on Number Lines
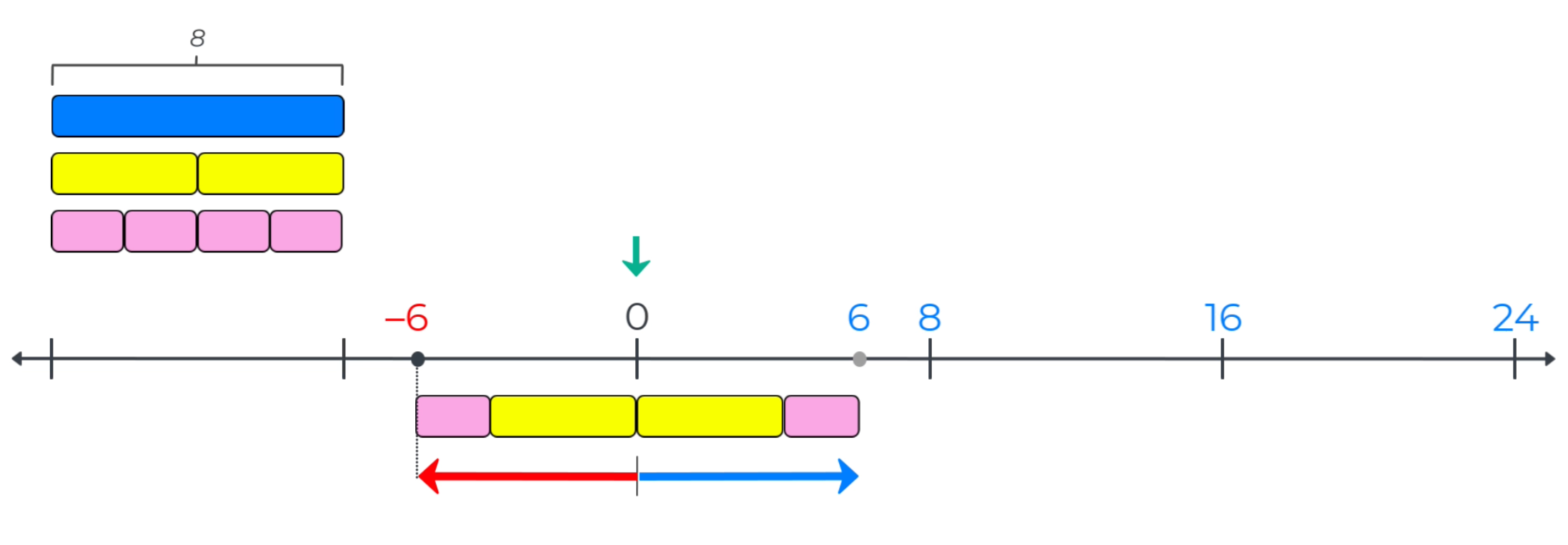
Once students have mastered the use of measurement strategies to locate whole (positive) numbers to the right of zero, negative numbers can be introduced as the reflection of positive numbers across the tick mark for zero.
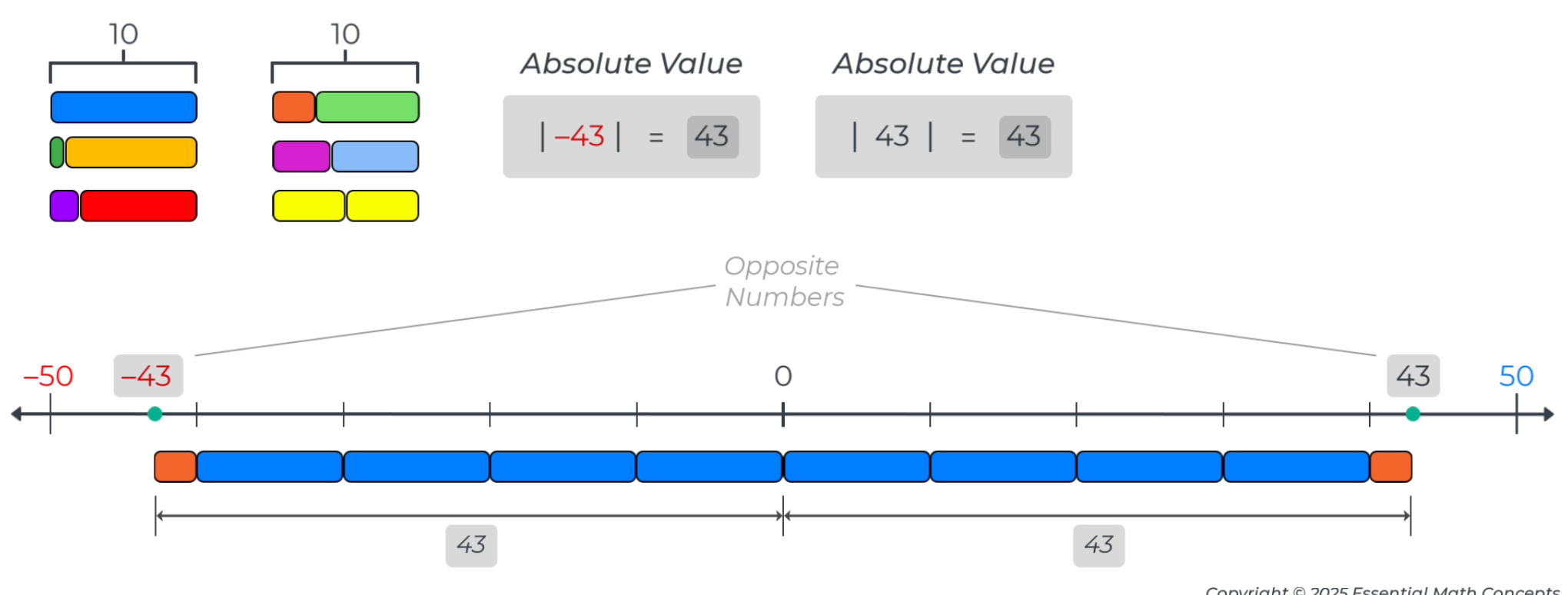
So, the measurement strategies used to locate and label whole numbers to the right of zero in grades 3-5 are used in grade 6 to plot positive integers to the right and negative integers to the left of zero. In addition, since the bars measure distance to both the right and left of zero, the length of a set of measurement bars used to measure from zero can be introduced as the absolute value of a number.
This application of measurement strategies to represent rational numbers means that assessing students’ knowledge of and ability to use measurement strategies to locate and label whole numbers is a good indicator of student preparedness to learn rational number concepts in Grades 6-8.
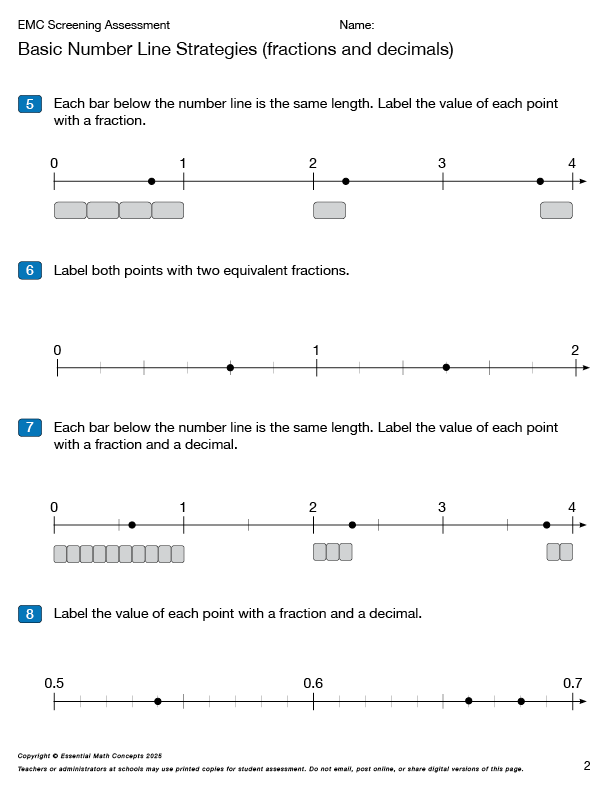
Assess Basic Number Line Strategies — Page 2 (Fractions and Decimals)
This 8-question screening assessment can be used to identify which basic number line strategies students are bringing with them into middle school. Students will need these number line strategies with whole numbers, fractions, and decimals to be prepared to represent rational numbers on number lines in grades 6 and 7.
Click on the image below and enter the password EMC to view and print these assessment pages.